How Tariffs, AI, and Robots Will Reshape Industry and Humanity
Tariffs are breaking old trade ties. AI and robots are rewriting the rules. The U.S.–China split is just the beginning of a new world map drawn in algorithms, not alliances.
At the very least $20 Trillion are at stake in the intersection of AI and Crypto. How are these two technologies headed and who is working to control these? This is a very deep analysis of the convergence.


There is a little-known story, tucked away in the memoirs of Felix Somary titled "The Sanjak Railway".
Now, remember that Somary had studied under the great Carl Menger, the father of Austrian economics for his PhD.
The year was 1908, and Somary had been tasked with syndicating a commercial loan to build a railroad from Bosnia to the Greek port city of Salonika, now known as Thessaloniki. The project itself was relatively insignificant, but it was the reaction it sparked that would prove to be a harbinger of things to come.
As Somary delved into the project's financial feasibility, he discovered that the proposed route would cross an Ottoman province called the Sanjak of Novi Bazar. This necessitated an application to the Sublime Porte for permission, a routine matter, or so it seemed.
But what happened next caught Vienna off guard. A storm of protest erupted from foreign ministries in Moscow to Paris, with the Russian-French alliance reacting with unprecedented intensity.
The Russians and French countered with a proposal of their own, a railway from the Danube to the Adriatic, a move that Somary recognized as a clear provocation. This was no ordinary diplomatic spat; it was a warning sign, a signal that the great powers of Europe were on a collision course.
Somary, with his keen analytical mind, inferred that if a minor incident like the Sanjak railway could elicit such a strong reaction, then it was only a matter of time before larger, more significant events would push the world to the brink of war.
He was not alone in his thinking; contemporary intelligence analysts would later come to recognize such incidents as "indications and warnings," precursors to greater conflicts.
But what's remarkable about Somary's insight is that it was rooted in a mathematical framework, one that would later become known as Bayesian statistics. He had, in effect, applied Bayes' theorem to the problem, starting with a hypothesis about the probability of world war, which, in the absence of any information, was weighted fifty-fifty. As incidents like the Sanjak railway emerged, they were added to the equation, increasing the odds of war.
It was a prophetic insight, one that would prove to be eerily accurate.
The Balkan Wars of 1912-13 were just around the corner, and the Great War itself would erupt six years later, in 1914. Somary's analysis had allowed him to see the writing on the wall, to recognize the inevitability of conflict before it became apparent to the rest of the world.
What we do takes a lot of work. So, if you like our content and value the work that we are doing, please do consider contributing to our expenses. Choose the USD equivalent amount in your own currency you are comfortable with.
Eric Schmidt, ex CEO of Google, discussed the details of where the AI is headed.
Schmidt discusses the concept of large context windows in AI and their impact.
He shares how they can enable models to process extensive input—sharing examples of companies advancing from hundreds of thousands to millions of tokens.
But there was one example which caught one's eye. How context windows can radically change the world we live in.
Before we go on, let us understand what are these context windows and AI agents?
And now the other concept - the AI Agents.
Now listen to this part of the video.
Eric Schmidt is pointing to a fundamental shift in the AI world and in how the models (LLMs) interact with commands.
He suggests that the world is moving from AI systems that merely process and generate text to AI systems capable of executing tangible, complex digital actions, which marks a profound evolution in artificial intelligence.
Currently, public AI systems, particularly large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, are primarily designed to engage in conversation, assist with information retrieval, or perform basic computational tasks. These models excel at understanding and generating human-like language but stop short of interacting with the digital world in a seamless, action-oriented manner.
But what is awaiting us is something very radical.
The entire Supply Chain department, the applications that the professionals use, and the interventions they make will be gone!
So you see, these future AI systems would be far more aware of the context within which they are operating. Whether it is managing business processes, customer interactions, or logistical operations, the AI would make informed decisions based on real-time data, user history, and global trends.
We are talking here about running the whole company in an autonomous manner!
Beyond just generating text or insights, the AI could interact with multiple software systems and interfaces, autonomously carry out decisions (e.g., adjusting inventory levels, placing orders, allocating budgets), and continuously learn from outcomes to refine its decision-making process.
All done flawlessly?!
Well, the ability of the AI systems to do work correctly is understood by a concept called Hallucinations.
Let us dig a little deeper into the concepts we discussed above.
Context windows are typically measured in tokens, which can represent words or parts of words. For example, GPT-3 has a context window of 2,000 tokens, while GPT-4 has a larger window of 32,000 tokens.
Larger context windows offer several advantages:
To get some .. well context to the Context Windows, let us see how they differ within the different models. Here is a list.
Note the rapid rise in the context windows between ChatGPT-3 and ChatGPT-Turbo.. and then Gemini 1.5 Pro!
So you see three things happen with larger context windows.
Balancing the context window size with application requirements and resource constraints is a crucial decision for AI developers. A larger context window enhances the model’s ability to handle complex, long-form tasks, but it also requires more resources and increases operational costs. By carefully considering the specific needs of the application and the limitations of available hardware, developers can strike a balance that maximizes performance while managing resource consumption. As AI models and hardware continue to advance, this balancing act will become easier, enabling more powerful and efficient AI systems capable of handling increasingly complex tasks.
So with two aspects - larger context windows and higher Text to Action complexities - we are looking at not just making an exponential change in what AI could do, but it will also be ensuring reduced AI Hallucinations.
"...well you have to assume that the current hallucination problems become less ... as the technology gets better and so forth I'm not suggesting it goes away and then you also have to assume that there are tests for efficacy so there has to be a way of knowing that the thing succeeded"
What does this all mean for the AI companies of the future?
Let's combine the power of the large context windows, the text-to-action transformations, and the ability of the AI to think on its own and we have a powerful set of systems on our hands.
Now add what OpenAI's Scott Aaronson (a theoretical computer scientist and Schlumberger Centennial Chair of Computer Science at the University of Texas at Austin) says about how AI can be used for creating biological and chemical weapons.
AI companies are engaging in AI "gain-of-function" research, that is aimed at enhancing the capabilities of artificial intelligence systems.
This research includes developing AI models that could potentially assist in dangerous and unethical activities, such as guiding the production of biological or chemical weapons.
Aaron's concern is that if AI systems are sophisticated enough to walk a user through every detailed step of creating a chemical weapon—offering precise instructions, identifying materials, and suggesting methods—this would pose an unprecedented security risk.
Such capabilities could be misused by malicious actors, including terrorists or rogue states, to manufacture weapons of mass destruction with ease and anonymity, amplifying global threats.
But based on Eric Schmidt's discussion earlier, we are now in a territory where the AI does NOT need to "walk humans through a process". It will do the process! At scale.
What if it is all done by an AI tool that is programmed to lie? Where propagandists who thrive on lying create the very core of this AI's moral code and data input?
That is precisely what Elon Musk discusses in a recent interview (May 2024).
The Gemini AI (Google's AI model) failed what is now being called the "Caitlyn Jenner test".
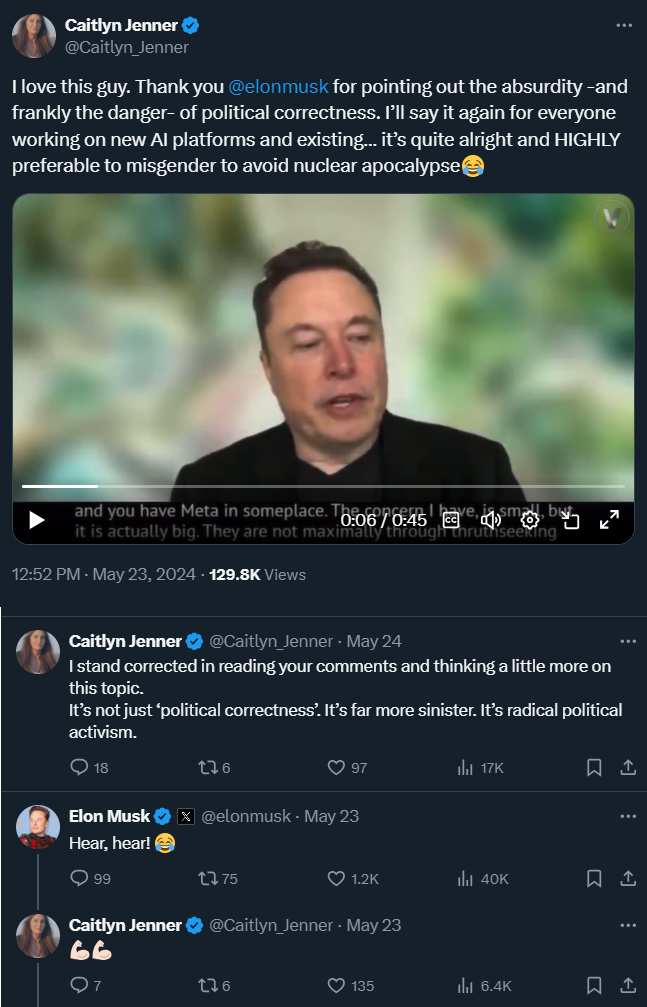
So think through it now.
AI models that pander to the data inputs that are built ground up on politically correct extreme woke ideologies rather than seeking "truth" or should one say facts (for in Dharmic terms Truth has a whole different meaning!) could come to conclusions which are bizarre because the ideology which lay at its foundation was fundamentally disingenuous or worse - complete lies.
It could, as Elon suggests, decide that "the best way to avoid misgendering could be to destroy all humans".
Here is one reminder of the impact that AI can have on the future of humanity. How many chances do humans have of survival?
AI's predictions and reasoning often mirror those of leading experts, such as Geoffrey Hinton (Turing Award winner), Ilya Sutskever (one of the most cited computer scientists), Max Tegmark (MIT professor), and Stuart Russell (author of a seminal AI textbook). This is likely because their research has been part of the AI's training data.
These thought leaders have issued grave warnings about the future of AI. In a recent video, Hinton's ominous remark that "we're not going to make it" may be a strategic use of language—what could be seen as a form of "prompt engineering" to influence the course of AI development.
Like Sutskever, Hinton has stepped away from his role to focus on AI safety, reflecting their concern for the future.
Both Hinton and Sutskever highlight that AI is not merely predicting the next word in a sequence; rather, it is developing a complex understanding of the world and reasoning through it—skills that are essential for accurate predictions.
This process allows AI to discover new insights by forging novel connections between existing pieces of data. However, this does not guarantee that the AI's conclusions are always accurate or well-founded. The inherent opacity of AI systems makes it difficult to fully understand or evaluate their reasoning processes.
These are all the dystopian outcomes that AI models could lead humanity to.
We may land there or we may change course.
But there is a far more credible impact of AI on us and our planet that we cannot avoid.
Irrespective of the direction of impact - which will be huge and profound - AI systems will require tremendous investments - in many billions!
Why?
Because we are talking about a phenomenal level of energy and water requirements to make that happen.
Take a listen first and then we can discuss.
As AI systems grow more complex and take on more advanced tasks, the need for larger datasets, faster processing, and higher levels of real-time computation will increase exponentially.
Companies will need large data centers and massive AI computational clusters to train and deploy these models. Energy availability will be a limiting factor in how quickly and efficiently companies can scale their AI capabilities.
Let us see the energy requirements as the chips improve.
Energy consumption is measured in Thermal Design Power (TDP). (Source: Datacrunch / Hyperstack)
Unlike current AI models, which are trained once and then deployed, future AI systems envisioned by Schmidt will need to be continuously learning and adapting to real-time data. This shift towards "always-on" AI will require constant access to high-performance hardware, increasing the energy burden significantly compared to current AI practices.
Large models, large inputs, and large data centers with "always-on" AI.
Now throw in the scenario where every aspect of life and business is managed via such complex AI models.
As AI expands across industries—running supply chains, handling autonomous systems, and even making strategic decisions for companies—energy will become a crucial resource.
By next year, it's estimated that approximately 3.5 million H100 GPUs will be deployed, consuming about 13,000 GWh of electricity annually. This is more than the annual power consumption of some entire countries, like Guatemala and Lithuania.

We are looking at a situation that will further impact the environment on this planet in a big way!
AI companies and businesses that depend on AI must ensure they have sustainable and scalable energy sources, especially as energy-intensive AI hardware becomes more pervasive.
So, if you think that the world is reeling in an energy crisis today, wait till we get to the future of AI.
Here is a sobering thought:
But it is not just the energy consumption that AI companies are grappling with. We are looking at substantial water consumption as well.
In their latest environmental reports, Microsoft Corp. and Google LLC – two of the leading players in the generative AI industry – reported a massive spike in the water consumption of their data centers, which experts attribute to the growing popularity of AI models. An article in the Associated Press published Saturday reported that Microsoft’s data center water use increased by 34% from 2021 to 2022. The company slurped up more than 1.7 billion gallons, or 6.4 billion liters, of water last year, which is said to be enough to fill more than 2,500 Olympic-sized swimming pools. It was a similar story with Google, which reported a 20% spike in its water consumption over the same timeframe. (Source: "Report: Data centers guzzling enormous amounts of water to cool generative AI servers" / Silicon Angle)
No wonder Schmidt talks about the US partnering even more closely with Canada.
Canada has about 20 percent of the planet's freshwater resources, sits astride the largest freshwater body of water in the world — the Great Lakes — and has so many power dams along its mighty rivers that when Canadians talk about electricity, they often just call it “hydro.” (Source: Washington Post)
But what that also means is that it will start a quest within the establishments of the major superpowers trying to steal these two resources - power and water - from other nations.
There is another revolution unfolding in the world of technology - Blockchain.
Let us look at that and its convergence with AI and see what it means for the world.
Earlier this year World Economic Forum shared an interesting perspective.
Looking ahead, the ideal state of convergence among blockchain, generative AI and spatial computing could transform societal structures in profound ways. Imagine a smart city where these technologies are fully integrated: Blockchain serves as the backbone for secure and transparent civic engagement, AI optimizes city services based on real-time data and spatial computing provides immersive, intuitive interfaces for citizens to interact with their urban environment. This could include everything from voting to urban planning, where citizens use AR interfaces to visualize and vote on city developments with the secure, immutable backing of blockchain technology, all enhanced by AI’s predictive capabilities to ensure sustainable and optimal planning. (Source: "Immersive technology, blockchain and AI are converging — and reshaping our world" / World Economic Forum)
This is the ideal world that the WEF article presents.
Is this being alarmist and conspiratorial?
Well, we have established the part (i) already to be true.
We know that blockchain and AI are converging.
So, the multi trillion-dollar question that we all need to now ask is "Can blockchain be hacked?"
Two young programmers from Microsoft had presented an interesting but geeky deck with just 9 slides in August 2007. Seemingly innocuous content with very far-reaching ramifications.
Here are the 9 slides.
So what did they say in layman's terms?
The Dual_EC_DRBG (Dual Elliptic Curve Deterministic Random Bit Generator) algorithm is a pseudorandom number generator (PRNG) that was designed to generate cryptographically secure random numbers. It was standardized by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2006 and was widely used in various cryptographic applications, including SSL/TLS and IPsec. The Dual_EC_DRBG algorithm is based on the mathematical concept of elliptic curves and uses two elliptic curves to generate random numbers. The algorithm takes a random seed as input and uses it to generate a sequence of random numbers.
Who could have inserted that backdoor into the Dual_EC_DRBG (Dual Elliptic Curve Deterministic Random Bit Generator) algorithm?
It was not until 2013 that the New York Times discussed the full spectrum of what the NSA had done concerning controlling the blockchain based on the leaks by Edward Snowden.
The agency has circumvented or cracked much of the encryption, or digital scrambling, that guards global commerce and banking systems, protects sensitive data like trade secrets and medical records, and automatically secures the e-mails, Web searches, Internet chats and phone calls of Americans and others around the world, the documents show. Many users assume — or have been assured by Internet companies — that their data is safe from prying eyes, including those of the government, and the N.S.A. wants to keep it that way. The agency treats its recent successes in deciphering protected information as among its most closely guarded secrets, restricted to those cleared for a highly classified program code-named Bullrun, according to the documents, provided by Edward J. Snowden, the former N.S.A. contractor. (Source: "N.S.A. Able to Foil Basic Safeguards of Privacy on Web" / New York Times)
The Snowden leak brought out the clandestine operation to create a backdoor by stealth - that was a partnership between the NSA and its British counterpart, Government Communications Headquarters, or GCHQ. Those who weren't briefed earlier were "gobsmacked"!
“For the past decade, N.S.A. has led an aggressive, multipronged effort to break widely used Internet encryption technologies,” said a 2010 memo describing a briefing about N.S.A. accomplishments for employees of its British counterpart, Government Communications Headquarters, or GCHQ. “Cryptanalytic capabilities are now coming online. Vast amounts of encrypted Internet data which have up till now been discarded are now exploitable.” When the British analysts, who often work side by side with N.S.A. officers, were first told about the program, another memo said, “those not already briefed were gobsmacked!” (Source: "N.S.A. Able to Foil Basic Safeguards of Privacy on Web" / New York Times)
So that was the NSA and its British counterpart.
Shuow and Ferguson found that the algorithm contained a set of constants that, if chosen in a specific way, could allow an attacker to predict the output of the PRNG.
The world has seen the impact of this backdoor covert control that the NSA has over cryptocurrencies. Contrary to the belief that they are untraceable, the fact is that they can be tracked - at least by Western intelligence agencies.
Criminals, often operating in hidden reaches of the internet, flocked to Bitcoin to do illicit business without revealing their names or locations. The digital currency quickly became as popular with drug dealers and tax evaders as it was with contrarian libertarians. But this week’s revelation that federal officials had recovered most of the Bitcoin ransom paid in the recent Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack exposed a fundamental misconception about cryptocurrencies: They are not as hard to track as cybercriminals think. On Monday, the Justice Department announced it had traced 63.7 of the 75 Bitcoins — some $2.3 million of the $4.3 million — that Colonial Pipeline had paid to the hackers as the ransomware attack shut down the company’s computer systems, prompting fuel shortages and a spike in gasoline prices. Officials have since declined to provide more details about how exactly they recouped the Bitcoin, which has fluctuated in value. (Source: "Pipeline Investigation Upends Idea That Bitcoin Is Untraceable" New York Times)
Not just the NSA, even the CIA is in with respect to interest in the world of cryptocurrency.
CIA Director William Burns has publicly confirmed that the agency is running several cryptocurrency-related projects. While the exact nature of these projects is not disclosed, Burns stated they are focused on:
Burns called cryptocurrency an "important priority" for the CIA and mentioned plans to devote resources and attention to the subject, including adding crypto experts to their team
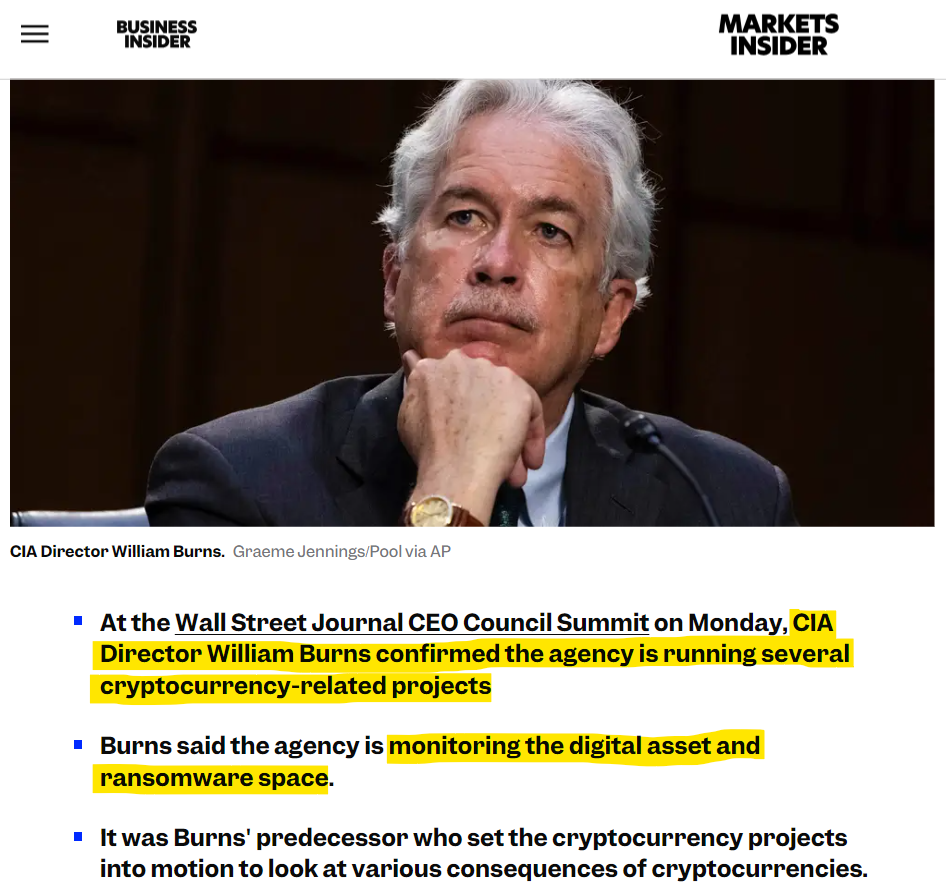
There is another angle to this: The use of cryptocurrencies in covert operations by the CIA and other intelligence agencies.
One of the primary advantages of cryptocurrency is its ability to facilitate clandestine operations. The CIA, for instance, has a long history of using various methods to fund its covert activities, from secretly owned banks to shell companies. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies offer a new level of anonymity and flexibility, making it easier for organizations like the CIA to move funds without being detected.
Do you see what can be done by someone who not only creates the building blocks of encryption but also the creation of certain cryptocurrencies - all in the name of transparency, security, and connectivity of course?
Now let us go to another side.
We will talk about a few companies and what they do. Pay close attention.
Ripple is a technology company that focuses on developing solutions for global payments. It is best known for its digital payment protocol and cryptocurrency, XRP. Ripple's primary goal is to enable secure, instant, and nearly free global financial transactions of any size with no chargebacks. The company aims to facilitate cross-border payments by providing a more efficient alternative to traditional banking systems, which often involve multiple intermediaries and can be slow and costly.
Ripple's technology is built on a decentralized, open-source protocol that allows for the seamless transfer of money in any form, whether it be dollars, euros, or cryptocurrencies. The company collaborates with financial institutions and payment providers to improve the speed and cost-effectiveness of international transactions. Ripple's network, known as RippleNet, connects banks, payment providers, and digital asset exchanges, enabling them to send money globally using blockchain technology.
Paxos is a financial technology company that focuses on building infrastructure for the global financial system using blockchain technology. The company aims to modernize and streamline the way financial assets are moved and settled. Paxos offers a range of services, including:
Polysign's primary aim is to offer institutional-grade custody solutions for cryptocurrencies and other digital assets, ensuring their safe storage and management.
The company is involved in developing advanced cryptographic and security technologies to facilitate the secure handling of digital assets. Polysign's subsidiary, Standard Custody & Trust Company, is a regulated entity that provides custody services, further emphasizing its focus on security and compliance in the digital asset space.
Polysign focuses on providing secure and scalable infrastructure for digital assets for institutional clients pprimarily. Here are the key services and offerings of Polysign:
Bottomline: Polysign claims to provide a robust and secure platform for the custody and management of digital assets, addressing the needs of institutional investors in the rapidly evolving cryptocurrency and blockchain space.
Dapper Labs is a company that focuses on developing blockchain-based products and experiences. It is well-known for creating CryptoKitties, one of the first blockchain games that allowed users to buy, sell, and breed virtual cats using cryptocurrency. This game was significant in demonstrating the potential of blockchain technology for creating unique, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) that represent digital assets.
Primarily, Dapper Labs is working at using blockchain technology to create new forms of digital interaction and ownership. It claims to bring blockchain to mainstream consumers through engaging and accessible applications
Mojaloop is an open-source software platform designed to facilitate interoperability between financial services providers, particularly in emerging markets. Its primary goal is to enable financial inclusion by making it easier for different financial systems to connect and work together, allowing for seamless transactions across various platforms. Mojaloop provides a framework for building digital payment systems that can connect banks, mobile money providers, and other financial institutions, thereby expanding access to financial services for underserved populations
Mojaloop works in emerging markets. These are the features of its platform:
Let's cut to the chase and see what Mojaloop is doing.
You may remember we had discussed UPI and the India Stack in a lot of detail.

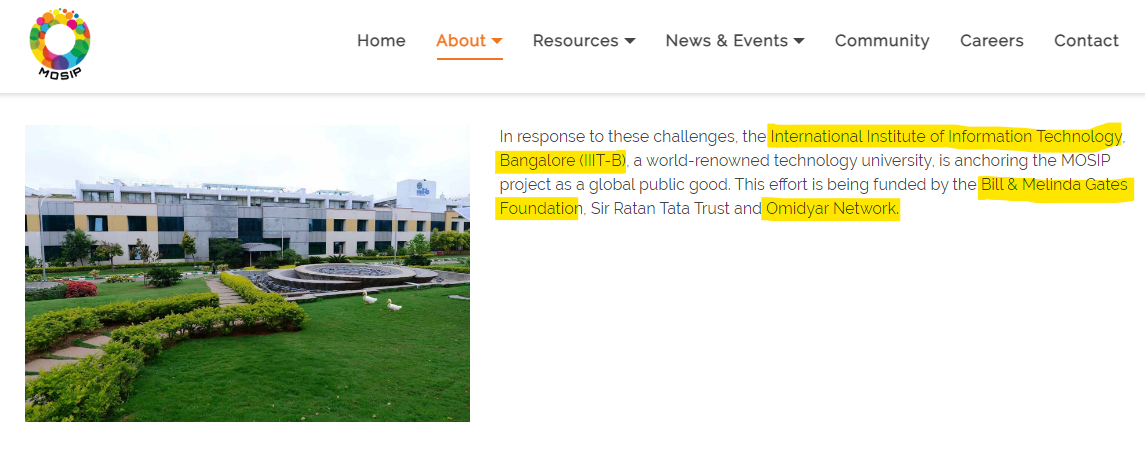
We had mentioned about Modular Open Source Identity Platform (MOSIP) in that discussion.
In 2018, the quest for creating an ID system to tag every person on the globe was undertaken after the Indian example of Aadhaar made waves across the world. The World Bank first approached the government for the Aadhaar framework but the Indian government did not share it since it was proprietary. It then went to the International Institute of Information Technology-Bangalore (IIIT-B) to create a system similar to Aadhaar.
Modular Open Source Identity Platform (MOSIP) was born out of that engagement.
Do you know who funded that research?
Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Omidyar Network.
And guess who funds Mojaloop?
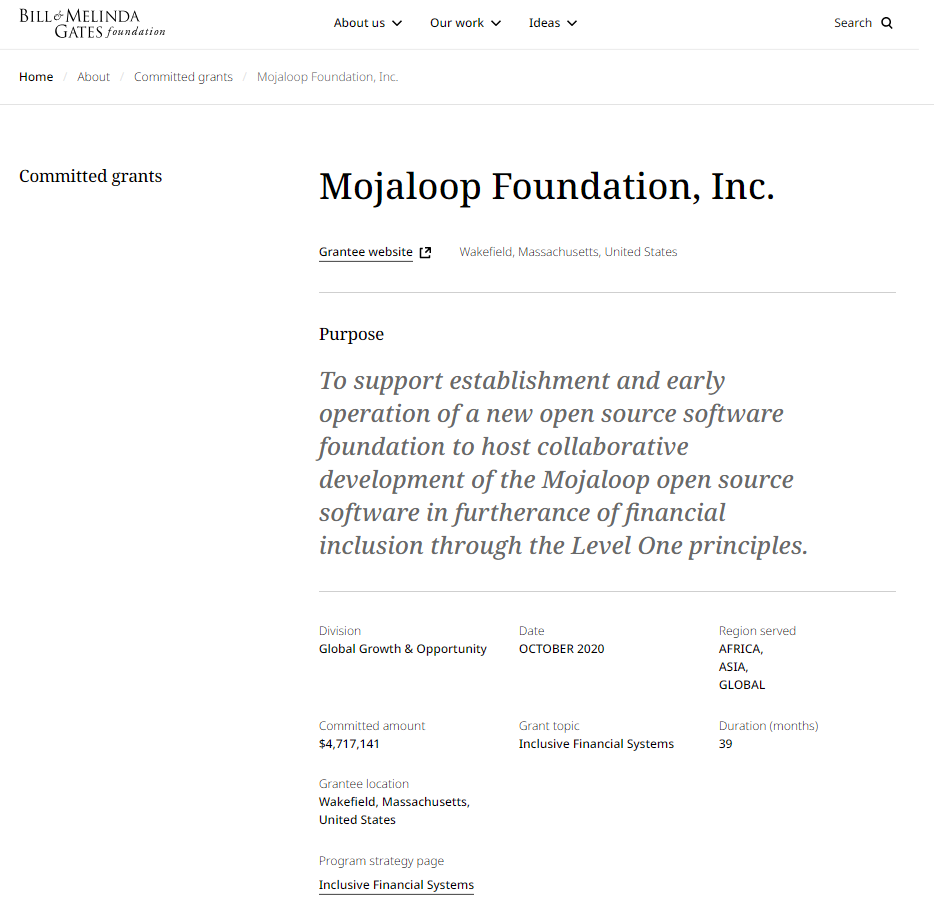
Hmmm... coincidence?
You may very well ask the question now -
Because they have a pattern.
Read this very interesting thread below. It shares connections between Soros, the Rothschilds, and the Rockefellers, as well as the companies they are jointly involved with. Also included is the connection of Jared Kushner - the Senior Advisor to ex-President Donald Trump.
Let's lay the whole pattern out.
We used AI to create a mind map of these connections. Not perfect but something that one can use to see the connections visually.
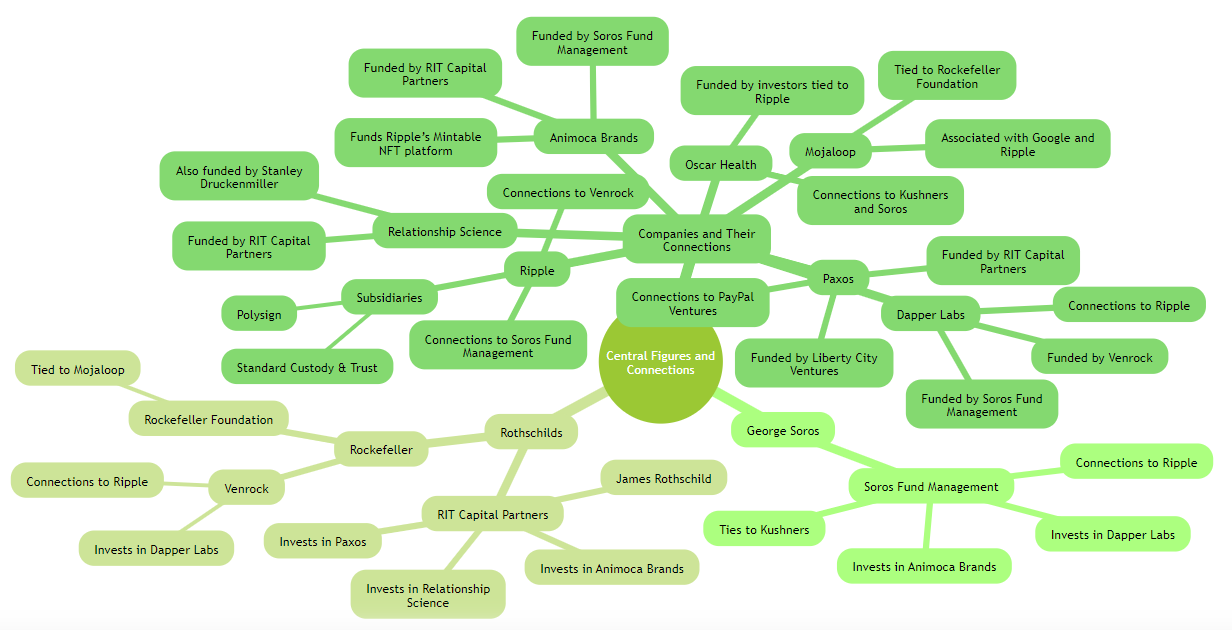
What does all this mean?
In all this, ultimately it is a race for global dominance by the wealthy such that they control the financial infrastructure of the world.
If they are the ones who construct it, then they control it.
That is quite substantial.

The key to this global dominance will be:
And lots of them!
So when you bring together the characters who personify the Deep State in a quest to define and control the next generation of blockchain and cryptocurrency architecture for global financial transactions, we are looking at those "indications and warnings," we discussed in the Somary story in the beginning.
Maybe nothing will come out of all this. But like Somary's story, at some point the strength of the hypothesis makes a consequent conclusion seem inevitable.
While some can see it as daylight, others equivocate.
So what are the ramifications of all this for any country or group that wants to enter into a world where AI and Crypto converge.
But first about just the AI world.
Any new competitor now needs these four major areas nailed down.
So when you think AI, do not think of one aspect. The barriers to entry in the AI world are rising exponentially.
And if you are not in the AI game in a leading position, then you are basically ready to be enslaved in the new colonial structures that will be erected in the coming century.
When the AI structures are combined with the blockchain world - we are looking at a world where the capital and financial infrastructure and money (digital) is controlled and programmed by a few - administered at will on others - while AI enables the rule in a very authoritarian world.
The window for entry is very small at the moment. If one misses it, one needs to be resigned to generations of modern-day robots like slavery.
Only a catastrophe at the planet level can stop such a colonial destiny for the billions in this world.