Trump’s Greenland Gambit: The Arctic Frontier and His Vision for a New Global Order
Trump has promised a new America. But the way he is approaching the world, he may up creating a new world order. His actions and words on Greenland need to be properly understood. Its a change in tactics but not a change in direction.

Changes are good.
Revolutions have often created new tyrannies that are worse than the previous ones.
One tyrant replaces another.
Analysis of human history reveals that radical and often violent revolutions have often replaced one form of authoritarian control with another, illustrating the cyclical nature of power dynamics.
Just look at these case studies of major revolutions that were radical and even violent.
French Revolution - Jacobins taking over from Bourbon Monarchy: The revolution sought "liberty, equality, fraternity," but the Jacobins instituted a totalitarian regime under the guise of protecting the revolution, suppressing dissent harshly.
- Old Fascists: The Bourbon monarchy under Louis XVI epitomized centralized autocracy, supported by a rigid feudal and aristocratic system.
- New Fascists: The revolutionary fervor culminated in the Reign of Terror (1793–1794) under the Jacobins, led by Robespierre. Political purges and widespread executions using the guillotine replaced aristocratic despotism with revolutionary authoritarianism.
Russian Revolution - Bolsheviks taking over from Tsars: The Bolsheviks promised workers' liberation but replaced aristocratic exploitation with state-driven repression, centralizing power under the Communist Party.
- Old Fascists: The Romanov dynasty represented oppressive autocracy with serfdom and stark inequality.
- New Fascists: After overthrowing the Tsar, the Bolsheviks, led by Lenin and later Stalin, established a one-party Communist state. Stalin's rule (1924–1953) was marked by purges, gulags, and the suppression of political freedoms.
Iranian Revolution - Khomeini took over from the Shah: While the revolution was initially framed as a fight for freedom and self-determination, it replaced one form of authoritarianism with another rooted in religious orthodoxy.
- Old Fascists: Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi ruled with Western-backed authoritarianism, secret police (SAVAK), and significant curtailment of political freedoms.
- New Fascists: The revolution brought Ayatollah Khomeini to power, replacing secular autocracy with a theocratic regime. The Islamic Republic imposed strict Sharia laws, suppressed dissent, and curtailed rights, especially for women and minorities.
Chinese Revolution - CCP took over from KMT: Promises of liberation for peasants and workers gave way to a personality cult, mass surveillance, and state-sponsored oppression.
- Old Fascists: The Kuomintang (KMT), led by Chiang Kai-shek, was marked by corruption, authoritarian control, and an inability to address the needs of the peasantry.
- New Fascists: The Communist Party of China (CPC), under Mao Zedong, established a regime with massive political purges (e.g., the Cultural Revolution) and a rigidly controlled society. The Great Leap Forward and the Cultural Revolution resulted in millions of deaths.
Cambodian Revolution - Khmer Rouge took over from Khmer Republic: The Khmer Rouge promised equality and a classless society but implemented policies that dehumanized and destroyed their own population.
- Old Fascists: The U.S.-backed Khmer Republic under Lon Nol was seen as corrupt and repressive.
- New Fascists: The Khmer Rouge, under Pol Pot, established one of the most brutal regimes in modern history. Nearly a quarter of Cambodia's population was killed in purges and forced labor camps.
Cuban Revolution - Castro took over from Batista: The revolutionary ideals of socialism and equality became overshadowed by state surveillance and imprisonment of dissidents.
- Old Fascists: Fulgencio Batista's dictatorship was characterized by crony capitalism, corruption, and suppression of political opposition.
- New Fascists: Fidel Castro and Che Guevara's revolutionary government promised freedom but quickly centralized power, suppressing dissent, and controlling every aspect of Cuban life.
Venezeula Revolution - Chavez took over from the Fourth Republic: The rhetoric of "power to the people" masked a descent into authoritarian control and economic mismanagement.
- Old Fascists: The political and economic elites of the Fourth Republic were accused of exploiting oil wealth while ignoring widespread poverty.
- New Fascists: Hugo Chávez’s Bolivarian Revolution initially aimed at empowering the poor but evolved into a highly centralized regime under Chávez and later Nicolás Maduro. Political opponents are jailed, media is suppressed, and the country faces economic collapse.
If we study carefully, we will see that the themes of every new tyrant who throws out the old one are very similar.
- Promise of Liberation: Most revolutions begin with the promise of freedom, equality, or justice for the oppressed.
- Centralization of Power: Revolutionary leaders often centralize power to "protect the revolution" from perceived threats.
- Silencing Dissent: Opposition is often branded as counter-revolutionary, leading to censorship, imprisonment, or execution.
- Cycle of Oppression: The oppressed frequently become the new oppressors, perpetuating the cycle of authoritarianism.
The questions one needs to see are:
- Are revolutions doomed to fail due to the inherent human tendency to seek control?
- Is gradual reform more sustainable than radical revolution?
How should one approach changes that will shift the society in a different direction?
If one has to bring radical changes, the people affecting them need to be of the highest integrity and wisdom. Aggression may be good, but arrogance and bullying can take society and new establishments down the old path.
Can the new Trump administration escape this curse?
Please Contribute to Drishtikone
What we do takes a lot of work. So, if you like our content and value the work that we are doing, please do consider contributing to our expenses. Choose the USD equivalent amount in your own currency you are comfortable with. You can head over to the Contribute page and use Stripe or PayPal to contribute.
I am thrilled to announce that I will be speaking at the Alternate Media Conference 2025 at the Constitution Club, New Delhi, on March 1-2. The theme for this year’s event is "Unstoppable Bharat", and the lineup of speakers is nothing short of extraordinary.

This is your chance to witness thought leaders, engage in transformative conversations, and interact directly with the speakers. Don’t miss this opportunity—grab your passes now: [Alternate Media Conference Passes].
Let’s come together to support independent voices and bold narratives.
Your donations to The Alternate Media can make it possible to host such impactful events. Be a part of this movement—donate generously and fuel the unstoppable rise of Bharat!
Send Donations to: Paytm : 9717753351 / Phonepay :9717753351 / Google Pay :9717753351 / Paypal : @thealternatemedia
The Phone Call That Shook the Trans-Atlantic
A phone call. Two leaders. A world watching.
The new US President, Donald Trump, called up Denmark’s Prime Minister, Mette Frederiksen, to discuss the future of Greenland, which he feels should be part of the United States.
Danish Prime Minister Mette Frederiksen and US President Donald Trump - what transpired between them? Words were exchanged, but what was indeed said?
Here is some idea.
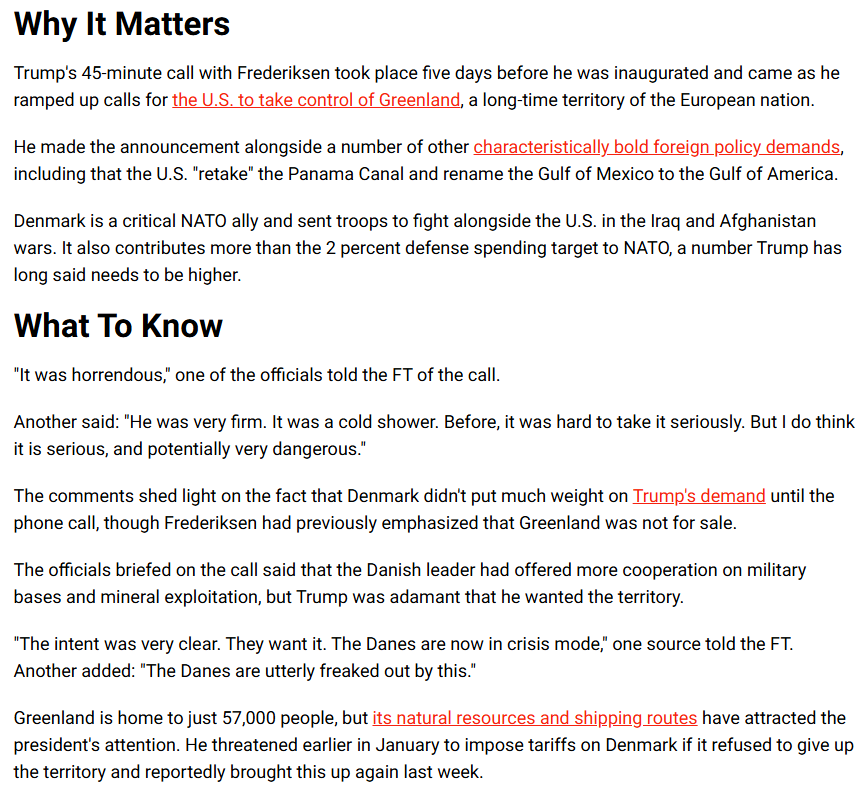
The conversation, we're officially told, was "constructive." But what does that mean in the language of diplomacy? Is it a veil for tension or a genuine bridge? Given the fallout, we know what that is anyway.
Greenland's Frederiksen was clear - "Greenland is not for sale."
This isn't the first time that the United States has wanted to 'buy' Greenland.
In 1868, the secretary of state William H Seward sought to purchase Greenland and Iceland for $5.5 million, envisioning them as vital outposts. While that deal faltered, interest persisted. In 1946, the US offered Denmark $100 million for Greenland, seeing it as essential for Cold War strategy. These historical attempts reflect America’s enduring interest in the Arctic. (Source: The wrangling over Greenland holds a mirror to modern geopolitics / Mail & Guardian)
But why Greenland?
Why Greenland - What Does it Offer?
Look, during the Cold War, Greenland was a central pillar of US defense planning against the Soviets.
A year after the Alliance was established, the U.S. Air Force secretly began work on Thule Air Base in Greenland, which became the most significant military installation in the territory. Commencing operations in 1952, Thule Air Base was a critical installation during the Cold War, hosting Strategic Air Command bomber and reconnaissance aircraft, as well as interceptors and Nike nuclear-tipped surface-to-air missiles. The Ballistic Missile Early Warning System (BMEWS) came to Greenland in 1961, when the BMEWS-Site 1 was established there, initially designated as the 12th Missile Warning Squadron and later the 12th Missile Warning Group. Air Force Space Command assumed control of Thule Air Base in 1983 and the unit was re-designated as the 12th Space Warning Squadron in 1992. In 1987, the BMEWS mechanical radar was upgraded to the more efficient and capable solid-state, phased-array system used today, the Upgraded Early Warning Radar (UEWR). (Source: Why Greenland Is Of Growing Strategic Significance / The Warzone)
Apart from security, it is home to a big cache of minerals - Oil & Gas to Rare Earths.
Rare earth elements: Greenland has some of the largest deposits of rare earth elements (REEs) in the world. These include yttrium, scandium, neodymium, and dysprosium. According to available data, Greenland is estimated to hold a significant amount of rare earth metal deposits, potentially ranking as the second largest reserve globally, with estimates suggesting around 42 million tonnes of Rare Earth Oxides (REOs). Some sources state that Greenland could possess roughly a quarter of the world's rare earth minerals.

Check this report out as well.
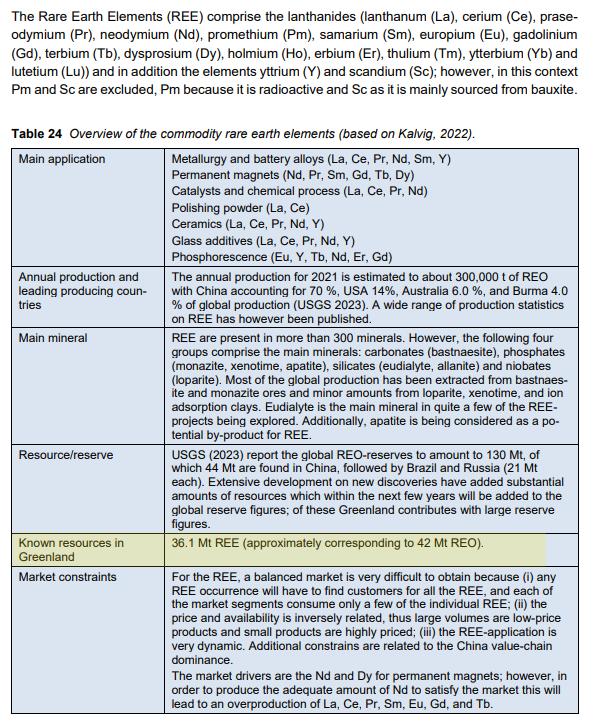
Trying to break away from China's stranglehold in the Rare Earth Minerals market is the key right now. And that is where Greenland becomes very important.
Access to Greenland's resources could help break U.S. dependency on China for rare earths. But already a Chinese state-owned company has more than a 12% stake in the Kvanefjeld deposit. Kvanefjeld is owned by Greenland Minerals, an Australian company, and China's Shenghe Resources is its largest shareholder and strategic partner. (Source: Greenland Is Not For Sale. But It Has Rare Earth Minerals America Wants / NPR)
Greenland is therefore, extremely critical in terms of the future semiconductor and also EV manufacturing.
- Oil & Gas: U.S. Geological Survey, Greenland is estimated to hold around 31,400 million barrels of oil equivalent (MMBOE) in oil, gas, and natural gas liquids, with the majority of this potential located in the East Greenland Rift Basins Province. (Source: USGS)
- Graphite: Graphite and graphite schist are found in many locations across the island.
Some Gold and Diamonds are there as well.
- Gold: Greenland has measured and indicated resources of 292,000 ounces of gold, and inferred resources of 718,000 ounces.
- Diamonds: Diamonds have been found in Greenland since at least the 1970s.
All this is now available for mining. As ice melts in the coming decades, Greenland can be a land of riches for many countries and companies.
Europe is looking to open a new frontier in the ever more urgent quest for new natural resources – the pristine icy wastes of Greenland. Oil and gas have been the focus of exploitation so far – but the EU sees just as much potential in a massive opening up of mining operations across the world's biggest island, according to Antonio Tajani, the European commission's vice-president and one of the most powerful politicians in the union. He called the move "raw material diplomacy". Latest satellite data reveal that 97% of the surface of the Greenland ice sheet underwent surface melting over four exceptionally warm days in July, indicating natural resources will become more available for extraction in the coming decades. The potential gold rush is being welcomed by some in Greenland, but has raised fears of environmental damage, pollution and despoliation across the Arctic that could destroy one of the world's last wildernesses. (Source: Europe looks to open up Greenland for natural resources extraction / The Guardian)
Billionaires like Jeff Bezos, Bill Gates, and Michael Bloomberg are increasingly involved in securing cobalt resources essential for lithium-ion batteries.
Traditionally, cobalt mining has been concentrated in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), a region plagued by ethical issues such as child labor and environmental degradation.
To mitigate these concerns and diversify supply chains, these investors are backing ventures like KoBold Metals, a U.S. technology firm employing machine learning to identify new cobalt deposits in areas like Greenland. This shift aims to ensure ethically sourced cobalt, reduce reliance on the DRC, and meet the surging demand driven by electric vehicles and consumer electronics. However, the endeavor underscores the complex balance between advancing clean energy technologies and addressing resource extraction's ethical and environmental challenges.
Read this report for more insights.

Greenland offers more than just minerals.
This island also offers a vantage for global security.
Greenland's strategic significance stems from its unique geographic position, making it a critical security asset for monitoring Arctic activities and defending North American interests. The island is an essential military outpost, providing unparalleled access to the Arctic's sea and air domains.
You see, that Thule Air Base that we discussed briefly above?
Well, in 2020, it became part of the United States Space Force. Then in 2023, it was renamed Pituffik Space Base.
Thule AB became part of the Space Force when the Armed Forces branch was established in 2019. In 2023, Thule AB was renamed Pituffik Space Base, after the former Inuit hunting settlement that was near the base's current location. Today, the space base has about 550 residents. (Source: What is the US Space Force doing in Greenland?Well, in 2020, it became part of the United States Space Force. / Space.com)
The Thule Air Base or the Pituffik Space Base (as it is now called) has regained strategic significance in the evolving geopolitical dynamics of the Arctic. Once a Cold War-era strategic location, the base now plays a renewed role in Arctic operations, reflecting its importance in an increasingly contested region.
Pituffik Space Base, formerly known as Thule Air Base, became part of Air Force Space Command in 1982. As of 2025, the base is home to the 821st Space Base Group, which is responsible for base support within the Pituffik Defense Area. The 12th Space Warning Squadron, a critical component of the base, operates a Ballistic Missile Early Warning Site designed to detect and track ICBMs targeting North America. This vital missile warning and space surveillance data is transmitted to NORAD command centers at Peterson Space Force Base in Colorado.
This needs to be seen in the context of Elon Musk's agenda of space superiority. Elon Musk's space plans include establishing a colony on Mars using SpaceX's Starship rocket.
SpaceX has ambitions to launch crewed missions to Mars as early as 2024 and currently has the field to itself, with no government agency or rival private company on course to challenge it. Such a plan would involve Mr Musk’s company building up to 100 Starships a year, with each one capable of housing 100 crew members and boasting “private cabins, large common areas, centralised storage, solar storm shelters and a viewing gallery”, according to SpaceX’s user guide for the rocket. (Source: Elon Musk reveals Starship progress ahead of first orbital flight of Mars-bound craft / Independent UK)
The base's strategic importance extends beyond missile defense. It also hosts Detachment 1 of the 23rd Space Operations Squadron, which is part of the global satellite control network. Pituffik Space Base operates various advanced weapons systems and maintains a substantial airfield with a 3,047 by 42 m (9,997 by 138 ft) asphalt runway, handling approximately 3,000 US and international flights annually
Pituffik remains a critical node in the U.S. Ballistic Missile Early Warning System (BMEWS), providing early detection of missile launches, particularly from polar trajectories.

Now, look at it again. The renaming to Pituffik Space Base underscores its expanded mission as a key U.S. outpost for space superiority, defense, and research in a rapidly contested Arctic environment.
Largely lost in the media furor, however, are the reasons why Greenland is vital for North American security. One of those reasons concerns the role of a crucial military installation on the world's largest island: Pituffik Space Base. "The Department of Defense has unveiled a new Arctic strategy, underscoring the region's critical importance to our national security and that of our allies," U.S. Space Force Chief Master Sgt. John Bentivegna said when he visited Pituffik in November 2024. Pituffik (pronounced bee-doo-FEEK) sits on Greenland's northwest coast, 700 miles (1,126 kilometers) north of the Arctic Circle. That's already a strategic location, and it's likely to become even more important as the Arctic warms and allows more shipping traffic, mining and other commercial activity, experts say. (Source: What is the US Space Force doing in Greenland? / Space.com)
Greenland was always critical for America's plans for not just the planet but also its space superiority.
Greenland and Control for the Arctic
Greenland’s strategic location, particularly with the Pituffik Space Base (formerly Thule Air Base), makes it a critical component in the future of Arctic Circle control. Positioned near the Norwegian Sea and the entrance to the North Atlantic Ocean, Greenland serves as a pivotal outpost for monitoring Arctic activities, securing sea lanes, and projecting power in the region.
In contrast, Russia’s current Arctic dominance, anchored by Kaliningrad near the Baltic Sea, relies heavily on its military installations, icebreaker fleet, and resource extraction infrastructure in the Arctic. Look at the map below. See where Kaliningrad is and where the Russian mainland is.
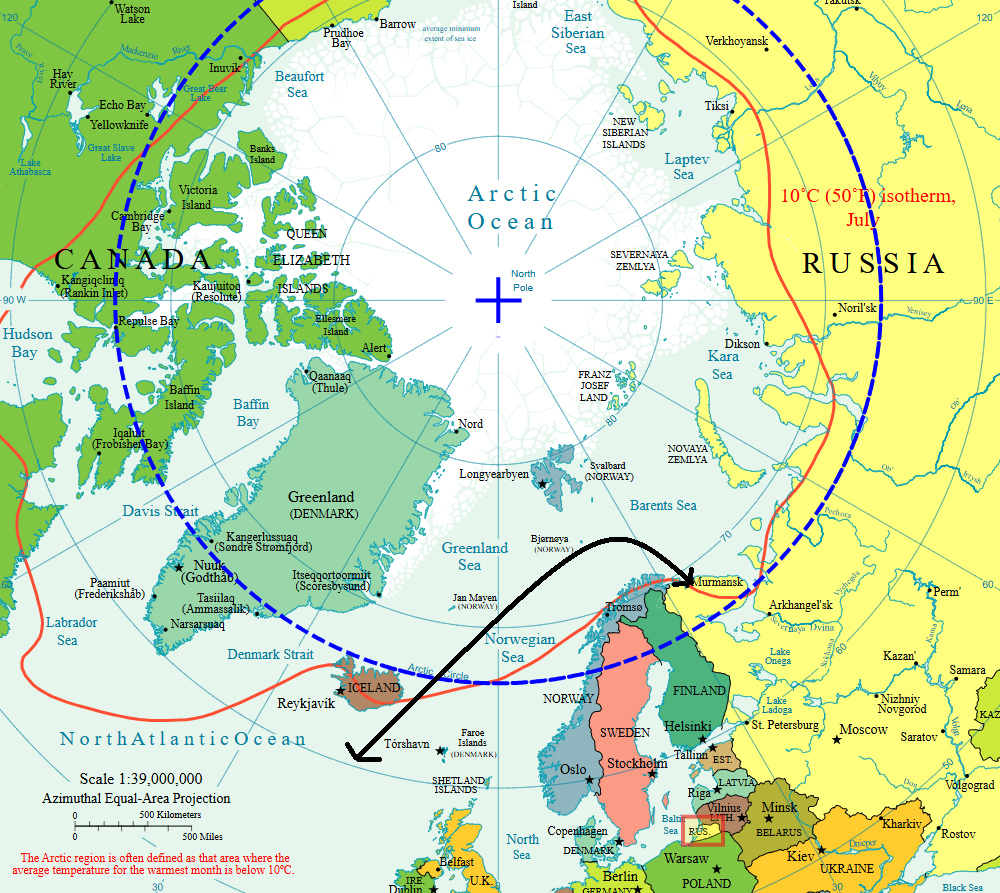
So if you carefully see, Greenland provides unparalleled access to monitor and potentially control North Atlantic sea routes and polar flight paths, which are becoming more critical as Arctic ice melts. Meanwhile, the Pituffik Space Base serves as a hub for early warning systems, space surveillance, and communication, strengthening U.S. dominance in polar-orbit satellite monitoring.
We have to factor in Russia's dominance of the Arctic. We have discussed that in detail in our article.

The critical factors are:
- The Northern Fleet and its significant icebreaker fleet, ensuring year-round access to Arctic waters.
- Military bases along the Northern Sea Route (NSR) and investments in hypersonic missile capabilities.
- Vast reserves of Arctic oil and gas are critical for its economy.
Let us get a reality check on the icebreaker fleet that Russia Vs. all other Arctic powers own.
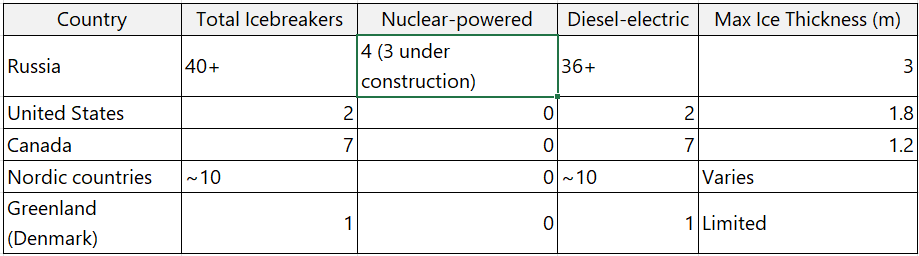
Clearly, Russia currently has dominance in the region vis-a-vis the NATO countries in the Arctic.
The China Factor
Meanwhile, China has invested in mining projects and infrastructure in Greenland, including efforts to access rare earth elements and establish footholds in the Arctic's economic landscape. Both Russia and China have pursued partnerships with Greenland to counterbalance U.S. influence, offering economic incentives to Greenland's semi-autonomous government.
Currently, China has been involved in multiple mining and icebreaking projects in Greenland, each with consequences. The Large Scale Project Act granted Greenland the authority to recruit foreign workers, which created concerns regarding the potential destabilization of the region due to an influx of Chinese workers. China’s rare earth project attracted controversy as developed countries sought to counter China’s dominance over the rare earths market. Greenland seems to be blinded by the goal of political autonomy from Denmark, and China has been able to gain a monopoly over the rare earth elements found in Greenland. The Arctic Yearbook analyzed the different possible drivers behind Chinese engagement in zinc mining and rare earth element mining projects in Greenland. Their conclusions suggested that “Chinese involvement in R.E.E. [rare earth elements] projects abroad are more likely to be driven by China’s interest in the strategic resource itself, whereas decisions of where to engage in zinc projects are more likely to be determined by China’s foreign policy priorities.” China has strategic goals that can be reached through the extraction of Greenland’s resources. (Source: The Organization for World Peace)
Beijing could leverage Greenland’s dependence on Chinese investments for mining projects to deter cooperation with Washington.
Russia and China have actively sought partnerships with Greenland, aiming to offset US influence in the region. They have offered various economic incentives to Greenland's semi-autonomous government, potentially swaying its allegiance.
A key concern is the possibility of cyber warfare and espionage targeting US installations, such as Pituffik. This could severely disrupt Arctic operations and compromise the integrity of US systems.
Furthermore, Russia may choose to bolster its military presence near Greenland's maritime boundaries. Such a move would challenge NATO operations in the region, complicating US logistics and supply chains. This would strain US-Greenland relations and heighten tensions between the US and Russia.
The race for Arctic control is intensifying as melting ice opens new sea lanes and access to untapped resources. Greenland is emerging as the linchpin of U.S. Arctic strategy, potentially challenging Russia’s dominance. However, Russia and China’s strategic investments in Greenland could serve as significant obstacles, leveraging economic and diplomatic means to stall U.S. efforts and maintain their foothold in the Arctic. For the U.S., forging stronger ties with Greenland’s government and maintaining robust NATO engagement will be essential to counterbalance these efforts and ensure long-term Arctic dominance.
The New Non-Diplomatic Foreign Affairs
Trump's style - brash, unconventional, unpredictable. How does it mesh with the measured tones of international relations?
The call clearly caused a significant furor in European capitals. They are "freaked" out.

The legitimate concerns about Denmark and Greenland's sovereignty aside, German Chancellor Olaf Scholz's comments sound very cute.
Till today, Europe runs roughshod over the sovereignty of other poorer countries. Its powers have no qualms about interfering with their governments and polity.
Of course, morality becomes an important consideration when the victim is a European country.
This response from Dr. Jaishankar to a question by a European journalist pretty much encapsulates the moral hypocrisy that has defined Europe for very long.
That issue with the European worldview is a reality is known. But let us get back to Europe's equation with the new US administration.
Trump has gone to the extent of threatening the use of military force against Greenland and even Panama.

This is a significant threat from a President who ran on the premise of stopping wars going forward.
Resistance to annexation actions
Despite Greenland's small and scattered population, external powers like Russia or China could covertly back resistance movements, aiming to entangle U.S. forces in prolonged conflict. Additionally, resistance might take the form of sophisticated cyber warfare, targeting and destabilizing U.S. Arctic operations.
A unilateral military action would provoke a significant backlash, particularly from Denmark (which governs Greenland) and the EU.
A U.S. intervention in Greenland could leave Washington diplomatically isolated, potentially uniting the EU and NATO in opposition to such actions. Meanwhile, Russia and China could seize the opportunity to strengthen ties with Denmark and other Arctic stakeholders, intensifying challenges for the U.S. and undermining its strategic objectives.
With Trump's style, aggression, and clear overt threats of annexation, Europeans are worried. They are contemplating hedging their geostrategic bets.
Two powers that come up in those calculations are - China and India.
But Trump’s rhetoric towards Europe has some wondering whether the continent should better hedge its bets. The new US president has threatened to take over Greenland, which belongs to Denmark, and has not ruled out using force. Tariffs could also be on the cards. “What I now see and hear from the incoming US administration is not promising for this special relationship [between Europe and the US], which has existed for so many years,” said Robert-Jan Smits, president of the executive board of Eindhoven University of Technology. “It might force Europe to look for other partners to cooperate with,” he warned.
The EU is already contemplating a broader pivot following Trump’s entry into office. Earlier this week, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen responded to Trump’s inauguration by saying that the EU needed to “engage beyond blocs and taboos.” The first trip of her second term will be to India, von der Leyen told delegates at the World Economic Forum in Davos. Meanwhile, she spoke relatively warmly about China, saying she wanted to “engage and deepen our relationship” and “expand our trade and investment ties.” “India is an obvious partner,” said Smits. Eindhoven, which is a key player in the global semiconductor industry, has stepped up its recruitment, both of staff and students, from the country. Trump’s rhetoric – threatening to take over Greenland through economic or military means, for example – also risks pushing Europe into reviewing its science cooperation policy with China, Smits said, although he stressed this should be “managed with great care, given the issue of knowledge security.” (Source: "How Trump could impact EU-US science and technology relations" / Science Bussiness)
So Trump's threats can have its own ramifications on the future geopolitical re-alignments.
The New Geostrategic realignments
That Trump's aggressive stance toward Greenland and his push to stop the war in Ukraine—actions that undermine European security priorities—create unease in Europe is obvious. Simultaneously, his administration's growing alignment with China and India signals a significant shift in U.S. foreign policy.
This realignment could reshape global geopolitics and further narrow America's strategic options.
Let us analyze.
Impact of EU-China Closeness on Geopolitics
If EU tilts towards China, it will change the chess pieces in the Atlantic and beyond.
Economic Dependency on China and Erosion of Transatlantic Unity:
- The EU has been dependent on the U.S. for security and stability since the Second World War, particularly against Russian aggression. Trump's distancing from European priorities weakens NATO cohesion, creating opportunities for China to deepen its influence in Europe through its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and economic partnerships.
- European countries might pivot to greater strategic autonomy, reducing reliance on the U.S. and potentially warming relations with China to safeguard their interests.
- European nations increasingly view China as an essential trade partner, particularly in green technologies and supply chains. For instance, Germany's reliance on China for industrial exports and the EU's ties through the Belt and Road Initiative highlight deepening economic interdependence.
- If Europe becomes more reliant on China for critical technologies like rare earths, EV batteries, and 5G infrastructure, it risks becoming vulnerable to Beijing’s economic leverage.
China's Leverage in Eurasia:
- The Breakdown of NATO cohesion could embolden Beijing to cement its dominance in Eurasia, leveraging economic and military influence. This weakens America's position in regions where China's sway is growing, such as Africa, Southeast Asia, and Central Asia.
- China's role as a mediator in conflicts, like Ukraine, would reinforce its image as a global peacemaker while sidelining U.S. leadership.
Undermining America's Indo-Pacific Strategy:
- The new re-alignment could impact the engagement of European powers in Quad Alliance (U.S., India, Japan, Australia) aimed at countering China's dominance in the Indo-Pacific.
China’s Strategic Gains in Europe:
- Beijing’s economic and diplomatic engagement in Europe, particularly through initiatives like the 17+1 Group in Eastern Europe (which is currently ineffective), allows it to divide EU consensus on critical geopolitical issues.
- Increased Chinese investment in European ports, energy infrastructure, and technology sectors bolsters China’s ability to project power in Europe and its periphery.
Economic Realignment:
- European nations might turn to China for investment and technology, further reducing U.S. influence in the region.
- As the Indo-Russia relationship strengthens and Trump threatens tariffs against China and India, things can further strengthen BRICS and create a counter to America.
Weakening Multilateralism:
- Trump's unilateral focus on China and India risks alienating smaller powers and allies, weakening multilateral institutions like the UN and WTO. This creates a vacuum that China could fill to advance its authoritarian governance model globally.
Strategic Implications for the U.S.
Reduced Global Influence:
- Closer ties with China could alienate longstanding European and Asian allies, eroding U.S. influence in multilateral forums and leaving it with fewer reliable partners in future conflicts.
Dependence on China:
- Engaging too closely with China might lead to strategic dependency, where U.S. leverage on issues like Taiwan, trade imbalances, and cybersecurity is diminished.
Geopolitical Isolation:
- By prioritizing China and India, the U.S. risks isolating itself from coalitions that have traditionally amplified its global power, particularly NATO and the G7.
Empowering Rivals:
- Cozying up to China could inadvertently strengthen its ability to challenge U.S. supremacy in critical areas like the Arctic, space, and global finance.
What does all this mean? Let us look at three possible scenarios.
Future Geopolitical Scenarios
- Scenario 1: Rising Sino-European Alignment: If European nations see the U.S. aligning with China, they may soften their stance toward Beijing to secure economic stability and hedge against U.S. unpredictability.
- Scenario 2: Strengthened Eurasian Bloc: Russia and China could solidify an anti-Western alliance, further isolating the U.S. and making it harder to project power in Eurasia.
- Scenario 3: U.S.-India Partnership Gains Momentum: While China's alignment with the U.S. might limit America's hard-power options, a deepening partnership with India could provide a counterbalance in Asia.
Europe’s growing closeness with China signals a rebalancing of global power dynamics, reducing America’s ability to maintain a united Western front against Beijing.
Don't Discount China.. Yet
There are many naysayers when it comes to China. Yes, it has a lot of issues. And yes, it has significant political, social and economic challenges.
But only fools will discount China as a power in the future.
When you see headlines like the ones we saw after DeepSeek was launched, you know that China is no longer just making cheap and lower-end stuff. It is in the race to the top and targeting top of the line sophisticated technologies. At a fraction of the cost that their Western counterparts have been able to create.

What does this mean for the world in the Trump era?
The Trump Era - Major Global Geopolitical Upheavals
With a hammer and a scythe at his disposal, Trump is out to change the global dynamics.
It's not as if the American establishment and military were not working on the Arctic strategy to contain and match Russia. They were.
Trump is making it more overt and in-your-face.
This leads to insults that have a more profound impact than some real hurts.
If this manner of engagement, along with Musk's swagger with respect to his own and his narrative's superiority, continues while dealing with the world, we may be looking at the creation of a new "Deep State." (Deep State 2.0)
It's not as if the current Deep State (Deep State 1.0) will vanish. It won't. It will simply shift its base.
From the US to Europe.
It is a gladiator's battle between Elon Musk and George Soros.

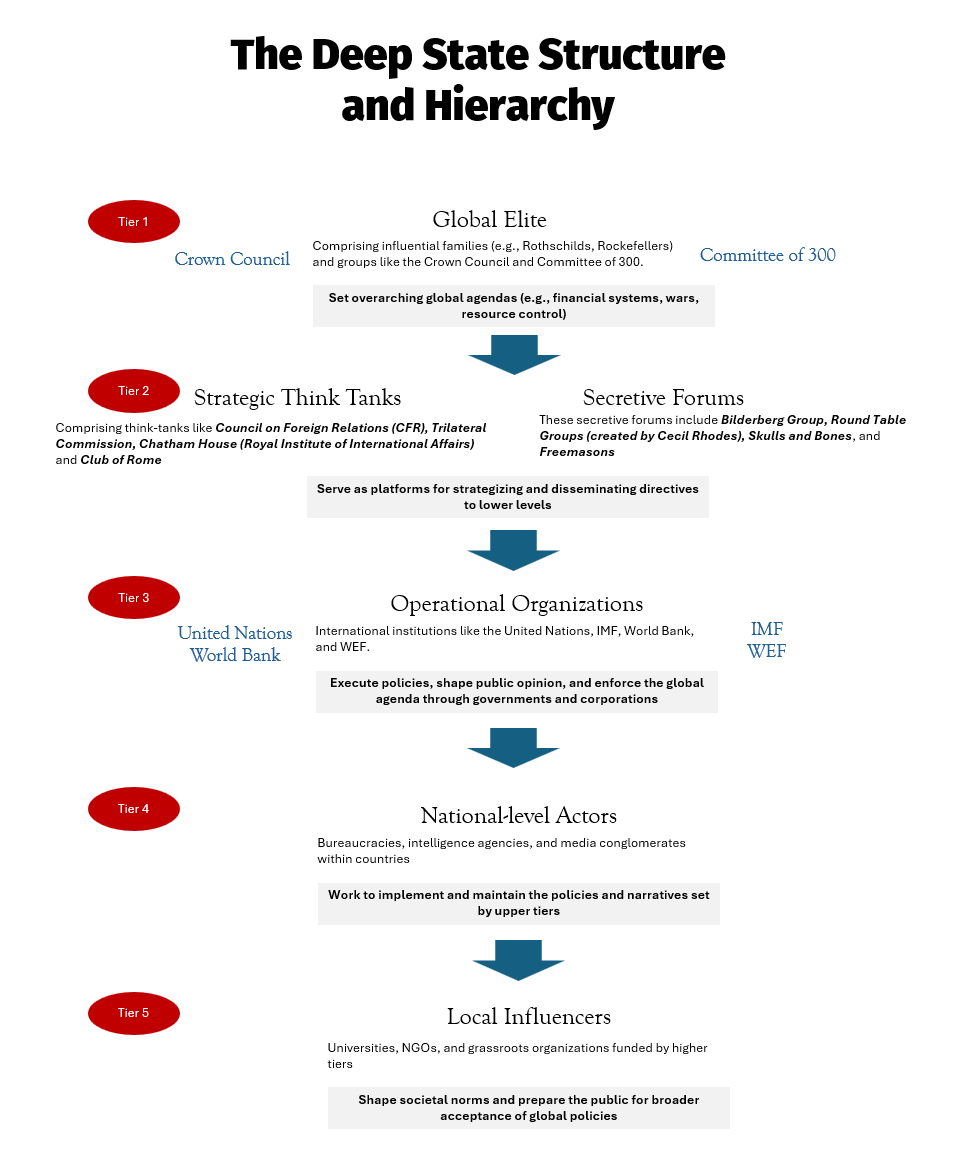
We had shared the five tiers of Deep State as we at Drishtikone see it.
Soros has operated at Tier 4 and Tier 5 originally and, in recent times, has taken over Tier 3 as well. The top two tiers remain intact.
Elon Musk may be more effective in carrying out the larger Deep State agenda. And with the level of his wealth, he may finally be at a point where he can challenge even Tiers 1 and 2 in the future.
With the Stargate controversy and differences of opinions surfacing between Elon Musk and Trump, things may not be very smooth when more contentious issues come and Trump asserts himself. Media spin and Deep State subversion pushing it further.

That will decide the effectiveness of the Trump administration and the geopolitical future for the world.







Comments ()